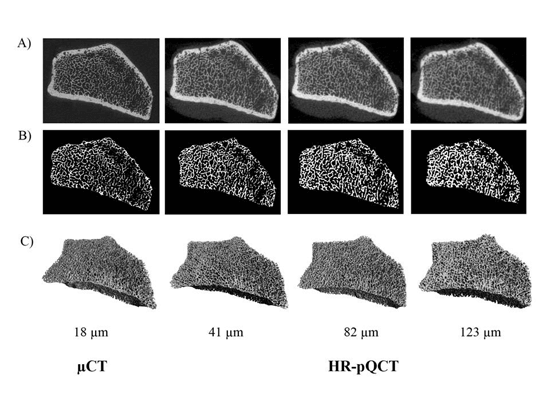
Accurate quantification of bone microarchitecture is significant in understanding bone mechanics and response to disease or treatment. High-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) allows for the quantification of trabecular and cortical structure in vivo, with the capability of generating images at multiple resolutions. The aim of this project is to characterize the effect of resolution on structural measures of trabecular and cortical bone and to determine accuracy in reference to micro-CT (µCT), the gold standard for bone microarchitecture quantification.