- This project proposed an effective and practical reconstruction pipeline to achieve motion-robust, multi-slice, real-time MR thermometry for monitoring thermal therapy in abdominal organs.
- The application includes a fast spiral MRI pulse sequence and a real-time reconstruction pipeline based on multi-baseline proton resonance frequency shift (PRFS) method with visualization of temperature imaging.
- The pipeline supports multi-slice acquisition with minimal reconstruction lag. Simulations with a virtual motion phantom were performed to investigate the influence of the number of baselines and respiratory rate on the accuracy of temperature measurement.
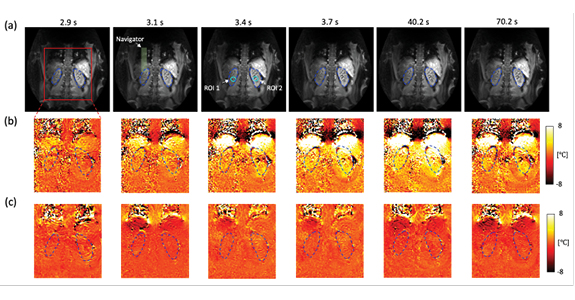
The result of healthy volunteer experiments without heating (volunteer #1). (a) A coronal slice is acquired and shows the left and right kidney organs which are indicated with blue dashed lines. PRFS temperature maps show that a (c) multi-baseline PRFS reconstruction allows stable and homogeneous temperature measurements, compared to a (b) single baseline
The result of healthy volunteer experiments without heating (volunteer #1). (a) A coronal slice is acquired and shows the left and right kidney organs which are indicated with blue dashed lines. PRFS temperature maps show that a (c) multi-baseline PRFS reconstruction allows stable and homogeneous temperature measurements, compared to a (b) single baseline
Motion phantom
- In this project, we developed a low-cost and simple MR-compatible respiratory motion simulator to support proof-of-concept studies of MR monitoring approaches with respiratory-induced abdominal organ motion.
- The phantom motion system integrates pneumatic control via an actuator subsystem located outside the MRI and coupled via plastic tubing to a compressible bag for distention and retraction within the MRI safe motion subsystem and phantom positioned within the MRI scanner.
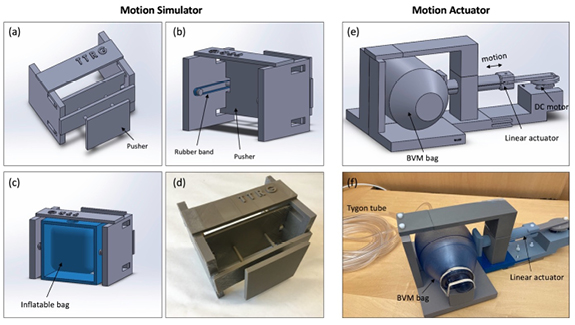
3D models and photos for the motion phantom and actuator.
Publication
- K. Kim, P. Jones, C. Diederich, E. Ozhinsky. Technical Note: Low-cost MR-compatible pneumatic respiratory organ simulator for development of MR-guided thermal therapy. Medical Physics, 00:1-7, 2022.
- K. Kim, C. Diederich, K. Narsinh, E. Ozhinsky. Motion-robust, multi-slice, real-time MR Thermometry for MR-guided thermal therapy in abdominal organs. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 40(1):2151649, 2023.