The simultaneous modality, PET/MRI, is a challenging environment due to the limitations of bringing PET and MRI together, but when appropriately leveraged, PET/MRI offers significant advantages over PET/CT. Nonetheless, significant work remains to move the field forward, and we are working at UCSF to help address these:
- Imaging of pulmonary nodules: due to the short T2* of lung parenchyma, PET/MRI struggles in the detection of small pulmonary nodules compared to CT. In oncology patients, pulmonary nodules are important and therefore many patients undergo an additional CT of the chest after imaging on a PET/MRI. We are evaluating novel short echo pulse sequences (UTE and ZTE) to improve the detection of pulmonary nodules in the setting of PET/MRI.
- Improved approaches to attenuation correction: in the setting of PET/CT, attenuation correction is relatively straightforward as CT is a near direct measure of density. In PET/MRI we cannot directly measure density and so other approaches have to be taken. The major issue is in imaging bone, which has characteristics that make it difficult to imaging using PET/MRI. Our initial work has been on using ZTE (zero echo time) MRI to allow for imaging of bone to improve attenuation correction maps for PET/MRI.
- Harmonization of quantitative accuracy: currently there are concerns about the quantitative accuracy of PET/MRI, primarily due to issues associated with attenuation correction. Additionally there are no methods to qualify PET/MRI scanners for clinical trials. Current phantoms used in PET/CT are not applicable for PET/MRI as they are not designed to be imaged using MRI. We are working on creating a PET/MRI phantom and methodologies to harmonize quantification across MRI platforms.
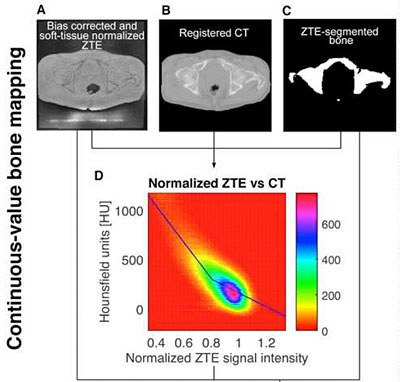
Creation of a hybrid ZTE + Dixon spoiled gradient echo attenuation correction map to allow for improved quantification of osseous lesions.
Clinical Trials
- Evaluation of Rectal Cancer Treatment Response Using PET/MRI (NCT02233595)
Publications
- Yang J, Yiqiang J, Jenkins N, Behr SC, Hope TA, Larson PEZ, Vigneron D, Seo Y. Quantitative evaluation of atlas-based attenuation correction for Brain PET in an integrated Time-of-Flight PET/MR imaging system. Radiology. 2017.
- Kluijfhout WP, Pasternak JD, Gosnell JE, Shen WT, Duh QY, Vriens MR, de Keizer B, Hope TA, Glastonbury CM, Pampaloni MH, Suh I. 18F Fluorocholine PET/MR Imaging in Patients with Primary Hyperparathyroidism and Inconclusive Conventional Imaging: A Prospective Pilot Study. Radiology. 2017 Jan 25:160768.
- Leynes AP, Yang J, Shanbhag DD, Kaushik SS, Seo Y, Hope TA, Wiesinger F, Larson PE. Hybrid ZTE/Dixon MR-based Attenuation Correction for Quantitative Uptake Estimation of Pelvic Lesions in PET/MRI. Med Phys. 2017.
- Hope TA, Verdin EJ, Bergsland EK, Ohliger MA, Corvera CU, Nakakura EK. Correcting for respiratory motion in liver PET/MRI: preliminary evaluation of the utility of bellows and navigated hepatobiliary phase imaging. EJNMMI Physics. 2015:2(1):21.
- Burris NS, Johnson KM, Larson PE, Hope MD, Nagle SK, Behr SC, Hope TA. Detection of Small Pulmonary Nodules with Ultrashort Echo Time Sequences in Oncology Patients by Using a PET/MR System. Radiology. 2016 Jan;278(1):239-46.